A type of cancer arising from the flattened epithelial cells that normally line the esophagus. This type of cancer is associated with smoking and alcohol consumption (among other factors such as genetics and anatomic abnormalities) rather than gastroesophageal reflux.
A margin refers to where the surgeon cut during the surgery. If the margin is positive, then there is tumor at the margin. If a margin is negative, then there is no tumor at the margin. The pathology report typically includes the distance of the tumor from each margin.
Cancer cells invading around nerves. This can be seen under the microscope.
Cancer cells invading blood vessels or lymphatic channels (which drain to lymph nodes). This can be seen under the microscope.
This term refers to how similar a cancer looks to the tissue of origin. Well differentiated adenocarcinomas form readily recognizable glands, while poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas do not.
This term refers to how similar a neoplasm looks to the tissue of origin. Low-grade neoplasms look more similar to the tissues from which they arose compared to high-grade neoplasms.
A classification system used to describe the extent of disease. In general, the lower the stage, the better the prognosis.
This is a new type of treatment, largely still experimental. Vaccines include whole killed cancer cells or specific proteins from the cancer, which are used to boost the body's immune system. Ideally, this will allow the body to fight and kill the cancer cells more effectively.
A painless procedure in which high frequency sound waves are used to generate pictures of the inside of the body.
Unable to be surgically removed.
The contents of the body above the diaphragm (a muscle flap above the abdomen). The thorax contains the heart, lungs, esophagus, and a variety of associated tissues.
A surgical incision of the chest.
Surgeon specializing in diseases of the thorax (the chest). The thorax contains the lungs, esophagus, heart, and a variety of associated tissues. Cardiothoracic surgeons operate on the heart and large blood vessels.
A hollow tube inserted into the body to relieve a blockage. A stent can be used to hold part of the esophagus open if the inside of the esophagus is narrowed due to a tumor.
A long (20 foot) tube that stretches from the stomach to the large intestine. It helps absorb nutrients from food as the food is transported to the large intestine. There are three sections: the duodenum, the jejunum, and the ileum.
An infection of the blood.
A malignant tumor that mimics connective tissues (bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, etc.) under the microscope.
Able to be removed surgically.
This term usually refers to the regurgitation of stomach contents into the esophagus. This causes heartburn and can even cause a laryngitis-like sensation. Patients with esophageal reflux are at increased risk of developing esophageal cancer.
The use of high-energy waves similar to x-rays to treat a cancer. Radiation therapy is typically used to treat a local area of disease and often is given in combination with chemotherapy.
The second part of the small intestine.
The first part of the small intestine.
A thick ring of muscle (sphincter) between the stomach and duodenum. This sphincter helps control the release of the stomach contents into the small intestine.
A class of powerful drugs which markedly reduce the ability of the stomach to produce acid. For patients with reflux (regurgitation, heartburn), these drugs can be extremely effective in reducing unpleasant symptoms, but these drugs do not reduce the possibility of developing cancer. Examples of proton pump inhibitors include: omeprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole, pantoprazole (not a comprehensive list).
A forecast for the probable outcome of a disease based on the experience of large numbers of other patients with similar stage disease. Importantly, determining a patient's prognosis is not an exact science. Some patients with poor prognosis beat the odds and live longer than anyone would have predicted.
A cancer found in the organ it started in. A primary cancer of the esophagus is one that started in the esophagus as opposed to a cancer that started somewhere else and only later spread to the esophagus.
A medical doctor specially trained to study disease processes. There are different types of pathologists. Anatomic pathologists typically look at biopsies or surgical specimens under the microscope to make diagnoses. Clinical pathologists specialize in managing laboratories that perform tests on samples (such as blood samples) from patients.
Any treatment that reduces the severity of a disease or its symptoms.
A surgically created opening in an organ that can also be referred to as an anastomosis.
A medical doctor who specializes in the treatment of tumors.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy given to patients before surgery. Some centers feel that the use of neoadjuvant therapy improves local and regional control of disease and that it may make more patients surgical candidates.
A mass or growth. This can be benign or malignant.
An abnormal proliferation of tissue that grows more rapidly than normal cells and will continue to grow if not treated. These growths will compete with normal cells for nutrients. This is a general term that can refer to benign or malignant growths. It is almost a synonym for the word tumor, which means a mass or growth.
An alteration in the DNA (genetic code) of a cell. Some mutations can lead to development of cancer.
A cancer that has spread from one organ to another. Cancers that have metastasized are generally not treated surgically, but instead are treated with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
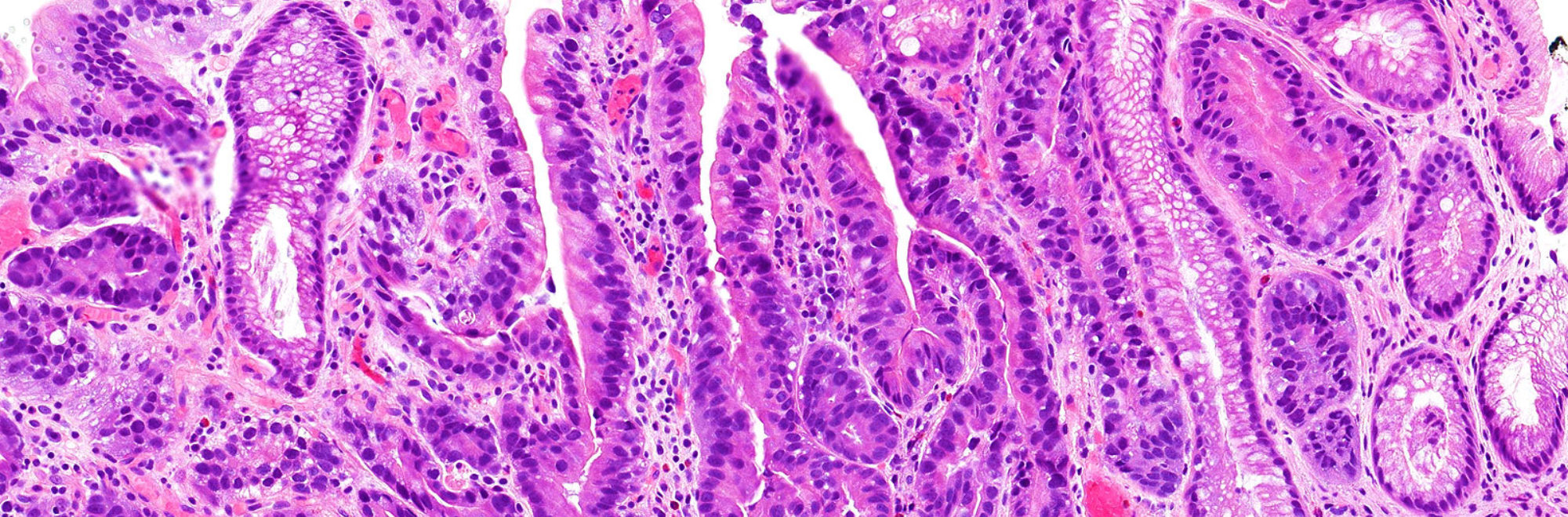
The replacement of the lining of an organ with the type of lining normally found in another site. In the esophagus, the normal lining is squamous epithelium, but in patients with reflux (regurgitation of stomach contents into the esophagus), the esophagus lining may be replaced with a cell type normally found in the intestines (intestinal metaplasia). Patients with intestinal metaplasia of the esophagus (Barrett's esophagus) are at an increased risk of developing cancer of the esophagus.
A cancer that has the potential of invading nearby tissues, spreading to other organs (metastasizing), and possibly leading to the patient's death.
A painless method for taking pictures of internal organs. A tube-like machine with a powerful magnet generates images of the inside of the body.
Normal, round, raisin- to grape-sized collections of lymphocytes (white blood cells) found throughout the body. Lymph nodes are connected to each other by lymphatic vessels. They normally help fight infection, but also are one of the first sites to which cancers spread. In general, the spread of cancer to lymph nodes portends a worse prognosis for the patient.
A primary cancer that has spread to regional lymph nodes and/or resectable (removable) tissues.
A technique that surgeons can use to visualize and even biopsy (take tissue samples of) organs inside of the abdomen without making large incisions. Some surgeons feel that this technique can help "stage" a patient less invasively than with open surgery.
A condition where the upper part of the stomach bulges through the diaphragm (muscle separating the organs in the chest and abdomen). This can result in reflux and heartburn symptoms.
A term used to indicate that cancerous cells are present in the lining of an organ but have not spread deeper.
A physician who specializes in digestive diseases, that is, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The gastrointestinal tract includes the esophagus, stomach, intestines, and anus. Some gastroenterologists also have expertise in diseases of the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas since these organs are also involved in digestion.
Referring to the stomach.
The hollow tube leading from the mouth to the stomach.
A procedure whereby a flexible fiberoptic tube is inserted into the esophagus, stomach or small intestine through the mouth (upper endoscopy) or into the large intestine through the anus (lower endoscopy) to look for abnormalities.
Surgical removal of a structure or part of a structure. For example, esophagectomy is removal of the esophagus and gastrectomy is removal of the stomach.
The type of tissue that normally lines the esophagus.
A precancerous condition in which cells which are very similar to cancer cells grow in an organ but have not yet acquired the ability to invade into tissue or metastasize (spread to areas distant from where they started). This is a stage which can be cured.
The part of every cell that carries all genetic information.
A dome-shaped muscle that separates the lungs and heart from the abdomen. This muscle assists in breathing.
A dye, taken by mouth or injected, that is sometimes used during x-ray examinations to highlight areas that otherwise might not be seen.
A type of cancer treatment that involves activating (turning on) a patient's immune system so that it is better able to recognize and fight cancer cells. Examples include: nivolumab, pembrolizumab, ipilimumab (not a comprehensive list).
Irritation of the esophagus due to regurgitation (reflux) of stomach contents into the esophagus. Patients with GERD can experience symptoms such as heartburn and are at increased risk of developing Barrett's esophagus.
Inflammation of the esophagus. This can occur due to reflux or other reasons such as infections or medications that irritate the esophagus.
A sample of tissue which is taken from an organ (such as the esophagus) and examined under a microscope. Barrett's esophagus and esophageal cancer can be diagnosed on biopsies.
A series of x-ray pictures taken by a machine that encircles the body like a giant tube. Computers are then used to generate cross-sectional images of the inside of the body.
The treatment of a cancer by chemicals. Examples include: fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, cisplatin, docetaxel, capecitabine, irinotecan, epirubicin (not a comprehensive list).
A type of cancer (malignant tumor) that arises from epithelium (the lining of an organ). Carcinomas that occur in the esophagus include adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma.
A cancer-causing agent.
A malignant tumor. It has the potential of invading into adjacent tissues and spreading to other organs.
Tumors which are non-cancerous. These generally grow slowly and do not invade adjacent organs or spread (metastasize).
A condition in which the normal lining of the esophagus is replaced by a type of lining normally found in the intestines (intestinal metaplasia). This is believed to be due to chronic reflux (regurgitation) of stomach contents into the esophagus.
A condition marked by a diminished apetite and aversion to food, which often results in physical signs of wasting.
A condition characterized by a deficiency in red blood cells. This can lead to fatigue among other symptoms.
A surgical joining of two hollow structures. It is similar to attaching two ends of a garden hose. For example, a gastrojejunostomy is a surgical procedure that connects the stomach and the jejunum (small intestine).
Chemotherapy given to patients after their cancers have been surgically removed. It is a secondary treatment given to supplement surgical treatment.
A type of cancer that can arise in Barrett's esophagus. Microscopically, adenocarcinomas form glands.
A pus-filled cavity.
The portion of the body between the diaphragm and the pelvis.